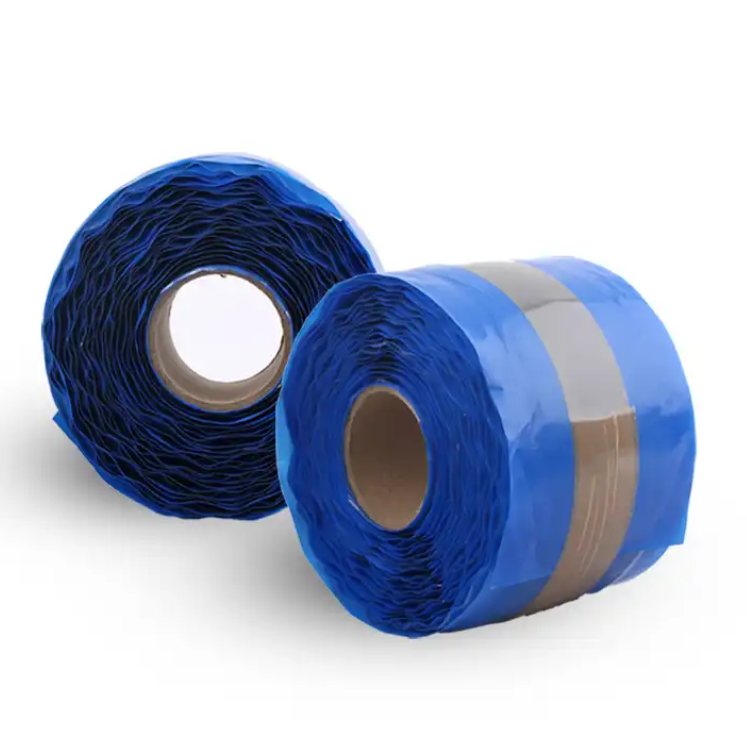
Which Glue Should You Choose for Hot Vulcanization Joints of Conveyor Belts?
2025-06-10 10:29:07In industrial production, conveyor belts play a crucial role in material transportation. The quality of conveyor belt joints is directly related to their operational stability and service life. Hot vulcanization joints are a common and effective connection method, and the selection of glue is of vital importance. Here, we recommend DG668 hot vulcanization adhesive, which stands out among many similar products.
I. The Powerful Performance of DG668
Extraordinary Adhesion: DG668 can penetrate deep into the fabric layers of conveyor belts and the gaps of steel wires, forming a tight bonding layer. It can firmly connect the joints of conveyor belts, whether they are made of rubber layers, fabric layers, or steel wire rope layers, ensuring that the joint parts fit closely with the main body of the conveyor belt. Even under long - term and high - intensity operation, it can maintain stable performance, significantly enhancing the strength and durability of the joints.
Excellent Temperature Resistance: It has a wide working temperature range and can withstand various harsh working conditions. In high - temperature environments, it will not soften or peel off; in low - temperature conditions, it still maintains good flexibility and adhesive effect, avoiding problems such as joint detachment or cracking caused by temperature changes. Its working temperature can reach 145°C, far exceeding that of ordinary adhesives.
Good Flexibility and Abrasion Resistance: During the operation of conveyor belts, they will constantly bend and deform. The good flexibility of DG668 enables it to adapt to various deformations, reducing the risk of joint cracking or detachment. At the same time, it has excellent abrasion resistance, maintaining outstanding performance even in harsh working conditions, extending the service life of the joints, and ensuring the stable operation of the conveyor belts.
II. Wide Range of Applications
DG668 is suitable for hot vulcanization joints of conveyor belts made of various materials, such as steel - fabric conveyor belts and fabric - layer conveyor belts. In industries such as coal mines, cement plants, mines, ports, metallurgy, and chemical engineering, in the face of high - wear, high - tension, and harsh working environments, DG668 can provide reliable solutions for conveyor belt joints.
III. Convenient Construction
The operation of using DG668 for joint bonding is not complicated. First, pre - treat the joint surface, removing impurities such as oil stains, dust, and rust, and sand it to increase the bonding area. Then, mix DG668 and the vulcanizing agent evenly in proportion, stirring quickly and thoroughly to avoid air bubbles. Next, evenly apply the prepared glue to the joint surface and the bonding surfaces of the unvulcanized core rubber and cover rubber, paying attention to controlling the thickness of the glue layer. After that, put the joint into a vulcanizer, heat it to 140 - 160°C, and maintain this temperature for 15 - 30 minutes to complete the vulcanization reaction. After vulcanization, let the joint cool naturally to room temperature, and then inspect it. A qualified joint should have a flat surface, no air bubbles, no cracks, and firm bonding.
IV. Environmentally Friendly and Safe
During the production and use process, DG668 has little impact on the environment and meets environmental protection requirements. Moreover, it has flame - retardant properties, which can enhance the safety of belt joints to a certain extent and reduce the risk of fire or explosion accidents.
In conclusion, with its excellent performance, wide applicability, simple construction process, and environmentally friendly and safe features, DG668 hot vulcanization adhesive becomes an excellent choice for glues used in hot vulcanization joints of conveyor belts, providing strong support for the efficient and stable operation of industrial production.
















.png)